# 双指针
# 0 思想
双指针问题的本质其实是由于有两个或者多个元素有相互作用或者相关联,因此在改变其中一个元素的同时其他几个元素也需要跟着改变,因此双指针问题一般是在满足几个元素关系不变的情况之下,改变一个元素的同时,寻找其他几个元素满足现有的关系情况。
1 首尾双指针

2 同向双指针
- 数组中,一般用于寻找满足某个条件的连续区间;
- 链表相关问题中经常会使用快慢双指针来寻找某个节点;
- 典型问题:最小覆盖子串、数组中的最长山脉(同向双指针)
3 反向双指针
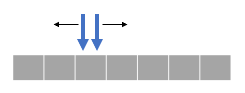
- 先依次遍历都某个节点,然后使用双指针从该节点反向判断是否满足条件。
- 典型问题:最长回文子串、数组中的最长山脉(反向双指针)
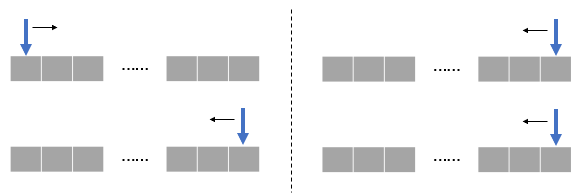
4 分离双指针
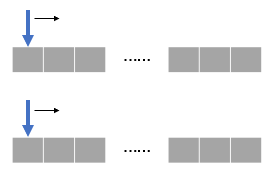
- 输入是两个数组/链表,两个指针分别在两个容器中移动;
- 根据问题的不同,初始位置可能都在头部,或者都在尾部,或一头一尾。
- 有序数组的 Two Sum
- 反转字符串中的元音字符
- 回文字符串
- 归并两个有序数组
- 判断链表是否存在环
- 最长子序列
# 1 首尾双指针
# 1 三数之和
给定一个包含 n 个整数的数组 nums,
判断 nums 中是否存在三个元素 a,b,c ,使得 a + b + c = 0 ?
找出所有满足条件且不重复的三元组。
注意:答案中不可以包含重复的三元组。
例如, 给定数组 nums = [-1, 0, 1, 2, -1, -4],
满足要求的三元组集合为:
[
[-1, 0, 1],
[-1, -1, 2]
]
- 思路 (1) 遍历数组的长度为n-2;至少需要留俩个位置lo, hi; 让 -arr[i] === arr[i+1]+arr[len-1];
- (2) 去重 第一次 从第一次遍历开始, 第二次找到答案后开始
var threeSum = function(nums) {
let ans = [];
const len = nums.length;
if(nums == null || len < 3) return ans;
nums.sort((a, b) => a - b); // 排序
for (let i = 0; i < len ; i++) {
if(nums[i] > 0) break; // 如果当前数字大于0,则三数之和一定大于0,所以结束循环
if(i > 0 && nums[i] == nums[i-1]) continue; // 去重
let L = i+1;
let R = len-1;
while(L < R){
const sum = nums[i] + nums[L] + nums[R];
if(sum == 0){
ans.push([nums[i],nums[L],nums[R]]);
while (L<R && nums[L] == nums[L+1]) L++; // 去重
while (L<R && nums[R] == nums[R-1]) R--; // 去重
L++;
R--;
}
else if (sum < 0) L++;
else if (sum > 0) R--;
}
}
return ans;
}
# 2 最接近的三数之和
给定一个包括 n 个整数的数组 nums 和 一个目标值 target。
找出 nums 中的三个整数,使得它们的和与 target 最接近。
返回这三个数的和。假定每组输入只存在唯一答案。
例如,给定数组 nums = [-1,2,1,-4], 和 target = 1.
与 target 最接近的三个数的和为 2. (-1 + 2 + 1 = 2).
- 比三数之和多了个比较, ans = Math.min( ans -t, sum - t);
class Solution {
public int threeSumClosest(int[] nums, int target) {
Arrays.sort(nums);
int ans = nums[0] + nums[1] + nums[2];
for(int i=0;i<nums.length;i++) {
int start = i+1, end = nums.length - 1;
while(start < end) {
int sum = nums[start] + nums[end] + nums[i];
if(Math.abs(target - sum) < Math.abs(target - ans))
ans = sum;
if(sum > target)
end--;
else if(sum < target)
start++;
else
return ans;
}
}
return ans;
}
}
# 3 颜色分类
# 2 同向双指针
# 1数组中的最长山脉
- 思路 (1) 找到 左山脉的起始点, 找到右山脉 的结束点,
- 可能有多个这样的山脉, 最大山脉 = Math.max(最大的山脉, 当前山脉)
我们把数组 A 中符合下列属性的任意连续子数组 B 称为 “山脉”:
B.length >= 3
存在 0 < i < B.length - 1 使得 B[0] < B[1] < ... B[i-1] < B[i] > B[i+1] > ... > B[B.length - 1]
(注意:B 可以是 A 的任意子数组,包括整个数组 A。)
给出一个整数数组 A,返回最长 “山脉” 的长度。
如果不含有 “山脉” 则返回 0。
示例 1:
输入:[2,1,4,7,3,2,5]
输出:5
解释:最长的 “山脉” 是 [1,4,7,3,2],长度为 5。
示例 2:
输入:[2,2,2]
输出:0
解释:不含 “山脉”。
提示:
0 <= A.length <= 10000
0 <= A[i] <= 10000
class Solution:
def longestMountain(self, A):
"""
:type A: List[int]
:rtype: int
"""
n = len(A)
res = 0
i = 1
while i < n:
l = i - 1 # 左山脚,注意 i 是从 1 开始的
while i < n and A[i] > A[i - 1]:
i += 1
if l == i - 1: # 不是山坡
i += 1
continue
r = i - 1 # 右山脚
while r < n - 1 and A[r] > A[r + 1]:
r += 1
if r == i - 1: # 不是山坡
i += 1
continue
else:
res = max(res, r - l + 1)
i = r + 1 #
return res
# 2 无重复字符的最长字串
给定一个字符串,找出不含有重复字符的最长子串的长度。
示例 1:
输入: "abcabcbb"
输出: 3
解释: 无重复字符的最长子串是 "abc",其长度为 3。
示例 2:
输入: "bbbbb"
输出: 1
解释: 无重复字符的最长子串是 "b",其长度为 1。
- 思路
- 1 双指针 + hash表, hash记录每个字母的位置, 遍历字符串: hash包含就记录(i)为起点+1;
- j 保存当前字符串的位置,每次遍历更新 Math.max(ans, j-i+1 ) ;
public class Solution {
public int lengthOfLongestSubstring(String s) {
int n = s.length(), ans = 0;
Map<Character, Integer> map = new HashMap<>(); // current index of character
// try to extend the range [i, j]
for (int j = 0, i = 0; j < n; j++) {
if (map.containsKey(s.charAt(j))) {
i = Math.max(map.get(s.charAt(j)), i);
}
map.put(s.charAt(j), j + 1);
ans = Math.max(ans, j - i + 1);
}
return ans;
}
}
- 思路 滑动窗口
- 1 双指针 +set ; 遍历字符串, 用字符串动态调整窗口(i, j)
- set不含有就add, j++; 含有remove,i++, 直到不含有;
class Solution {
public int lengthOfLongestSubstring(String s) {
HashSet<Character> set =new HashSet<>();
int i = 0, j=0, ans= 0;
int n = s.length();
while(i < n && j <n){
if(!set.contains(s.charAt(i))){
set.add(s.charAt(i++));
ans = Math.max(ans, i-j);
}else{
set.remove(s.charAt(j++));
}
}
return ans;
}
}
# 3 分离双指针
# 1两个数组的交集
给定两个数组,编写一个函数来计算它们的交集。
示例 1:
输入: nums1 = [1,2,2,1], nums2 = [2,2]
输出: [2]
示例 2:
输入: nums1 = [4,9,5], nums2 = [9,4,9,8,4]
输出: [9,4]
说明:
输出结果中的每个元素一定是唯一的。
我们可以不考虑输出结果的顺序。
思路
- 1)排序 + 二分
- 2)Hash
- 3)排序 + 双指针
class Solution:
def intersection(self, A, B):
"""
:type A: List[int]
:type B: List[int]
:rtype: List[int]
"""
A.sort()
B.sort()
m = len(A)
n = len(B)
res = []
i, j = 0, 0
while i < m and j < n:
if A[i] < B[j]:
i += 1
elif A[i] > B[j]:
j += 1
else:
if (i > 0 and A[i - 1] == A[i]) or (j > 0 and B[j - 1] == B[j]): # 去重
pass
else:
res.append(A[i])
i += 1
j += 1
# i += 1
# while i < m and A[i - 1] == A[i]:
# i += 1
# j += 1
# while j < n and B[j - 1] == B[j]:
# j += 1
return res
# 2 归并两个有序数组
Input:
nums1 = [1,2,3,0,0,0], m = 3
nums2 = [2,5,6], n = 3
Output: [1,2,2,3,5,6]
题目描述:把归并结果存到第一个数组上。
需要从尾开始遍历,否则在 nums1 上归并得到的值会覆盖还未进行归并比较的值。
nums1 = [1,2,3,0,0,0], m = 3
nums2 = [2,5,6], n = 3
Output: [1,2,2,3,5,6]
题目描述:把归并结果存到第一个数组上。
需要从尾开始遍历,否则在 nums1 上归并得到的值会覆盖还未进行归并比较的值。
public void merge(int[] nums1, int m, int[] nums2, int n) {
int index1 = m - 1, index2 = n - 1;
int indexMerge = m + n - 1;
while (index1 >= 0 || index2 >= 0) {
if (index1 < 0) {
nums1[indexMerge--] = nums2[index2--];
} else if (index2 < 0) {
nums1[indexMerge--] = nums1[index1--];
} else if (nums1[index1] > nums2[index2]) {
nums1[indexMerge--] = nums1[index1--];
} else {
nums1[indexMerge--] = nums2[index2--];
}
}
}
# 4 链表
# 1. 判断链表是否存在环
使用双指针,一个指针每次移动一个节点,一个指针每次移动两个节点,如果存在环,那么这两个指针一定会相遇。
public boolean hasCycle(ListNode head) {
if (head == null) {
return false;
}
ListNode l1 = head, l2 = head.next;
while (l1 != null && l2 != null && l2.next != null) {
if (l1 == l2) {
return true;
}
l1 = l1.next;
l2 = l2.next.next;
}
return false;
}