# Heap
# 1 heap idea
# 1 Application and implement
- 10 亿数字中最小的10个数字
- Computer networks. [ web cache ]
- Operating systems. [ load balancing, interrupt handling ]
- Data compression.
- Priority queue: Remove the largest (or smallest) item. add item into heap
# 2 Binary min-heap: Binary tree that is complete and obeys min-heap property.
- Min-heap: Every node is less than or equal to both of its children.
- Complete: Missing items only at the bottom level (if any), all nodes are as far left as possible.
#
# 2 Tree 表示
# 1 binarytree heap
# 5 最大堆
- Proposition: Largest key is a[1], which is root of binary tree.
- Proposition: Can use array indices to move through tree.
- ・Parent of node at k is at k/2.
- ・Children of node at k are at 2k and 2k+1
# 2 操作
- Insert: Add node at end, then swim it up.
- Remove the maximum: Exchange root with node at end, then sink it down.
public void insert(Key x)
{
pq[++n] = x;
swim(n);
}
# 3 由下至上的heap有序化(swim)
private void swim(int k){
while (k > 1 && less(k/2, k)){
exch(k, k/2);
k = k/2;
// 比较最后加入的与到root的位置路径上的值
}
}
# 4 由上至下的heap有序化(sink)
private void sink(int k){
while (2*k <= n){
int j = 2*k;
if (j < n && less(j, j+1)) j++;
if (!less(k, j)) break;
exch(k, j);
k = j;
// 比较由尾节点加入到root的位置, 让root(尾节点) 节点到适合的位置
}
}
# 5 delete
public Key delMax(){
Key max = pq[1];
exch(1, n--);
sink(1);
pq[n+1] = null;
return max;
}
# 6 实现
public class MaxPQ<Key extends Comparable<Key>>{
private Key[] pq;
private int n;
public MaxPQ(int capacity){
pq = (Key[]) new Comparable[capacity+1];
}
public boolean isEmpty(){
return n == 0;
}
public void insert(Key x){
pq[++n] = x;
swim(n);
}
private void swim(int k){
while (k > 1 && less(k/2, k)){
exch(k, k/2);
k = k/2;
}
}
private void sink(int k){
while (2*k <= n){
int j = 2*k;
if (j < n && less(j, j+1)) j++;
if (!less(k, j)) break;
exch(k, j);
k = j;
}
}
public Key delMax(){
Key max = pq[1];
exch(1, n--);
sink(1);
pq[n+1] = null;
return max;
}
private boolean less(int i, int j){
return pq[i].compareTo(pq[j]) < 0;
}
private void exch(int i, int j){
Key t = pq[i]; pq[i] = pq[j]; pq[j] = t;
}
}
# 3 heapsort
- 堆构造阶段: 从右到左利用sink()构造子堆。从右中点sink()到左, 一半的有序, 后半部分就是叶子节点
- 下沉排序:
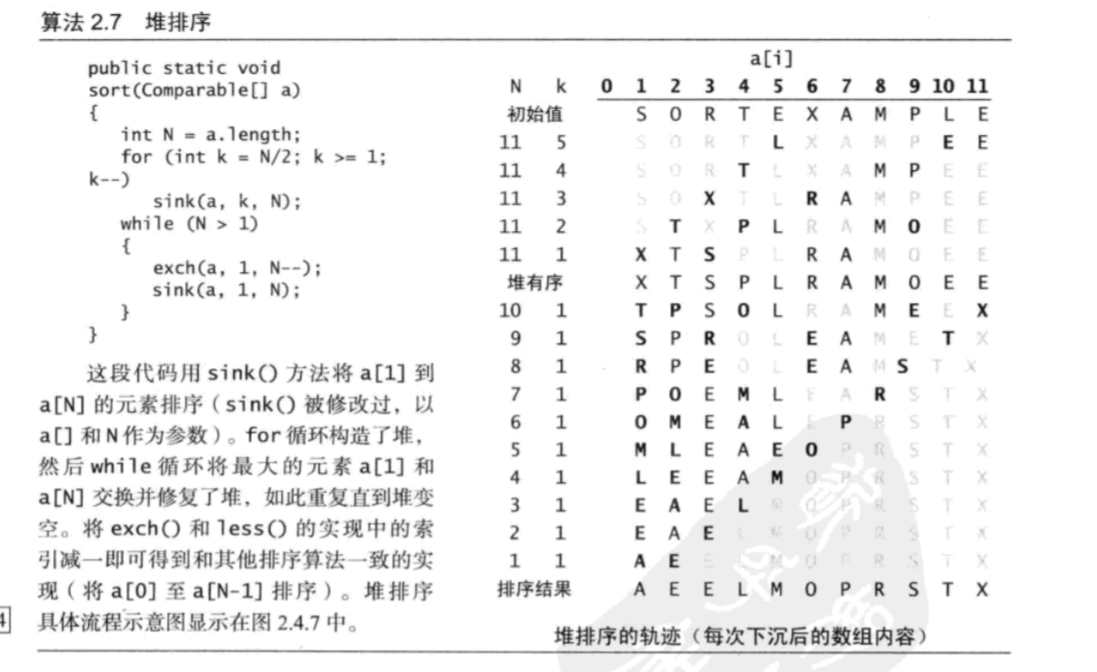
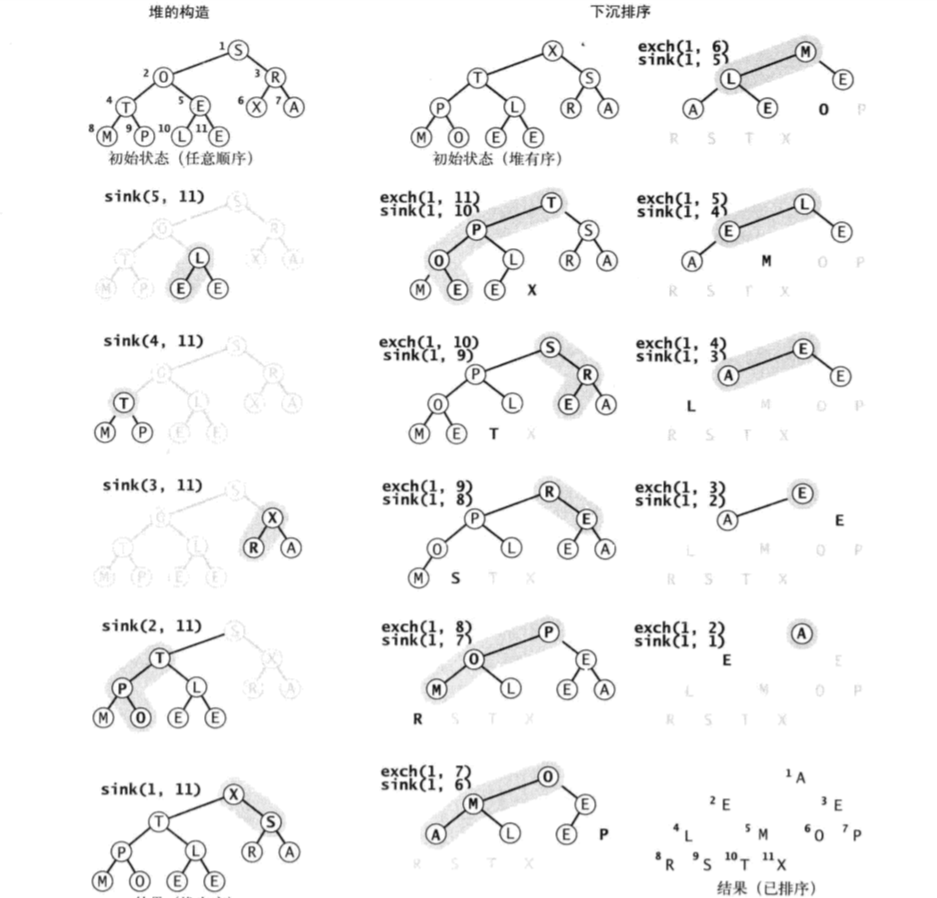
public class Heap{
public static void sort(Comparable[] a){
int n = a.length;
for (int k = n/2; k >= 1; k--)
sink(a, k, n);
while (n > 1){
exch(a, 1, n);
sink(a, 1, --n);
}
}
private static void sink(Comparable[] a, int k, int n){ /* as before */ }
private static boolean less(Comparable[] a, int i, int j)
{ /* as before */ }
private static void exch(Object[] a, int i, int j)
{ /* as before */ }
}
# 4 summary
# 1 BST vs Heap vs Array
| Ordered Array | Bushy BST | Hash Table | Heap | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| add | Θ(N) | Θ(log N) | Θ(1) | Θ(log N) |
| getSmallest | Θ(1) | Θ(log N) | Θ(N) | Θ(1) |
| removeSmallest | Θ(N) | Θ(log N) | Θ(N) | Θ(log N) |
| Name | Storage Operation(s) | Primary Retrieval Operation | Retrieve By: |
|---|---|---|---|
| List | add(key)insert(key, index) | get(index) | index |
| Map | put(key, value) | get(key) | key identity |
| Set | add(key) | containsKey(key) | key identity |
| PQ | add(key) | getSmallest() | key order (a.k.a. key size) |
| Disjoint Sets | connect(int1, int2) | isConnected(int1, int2) | two int values |
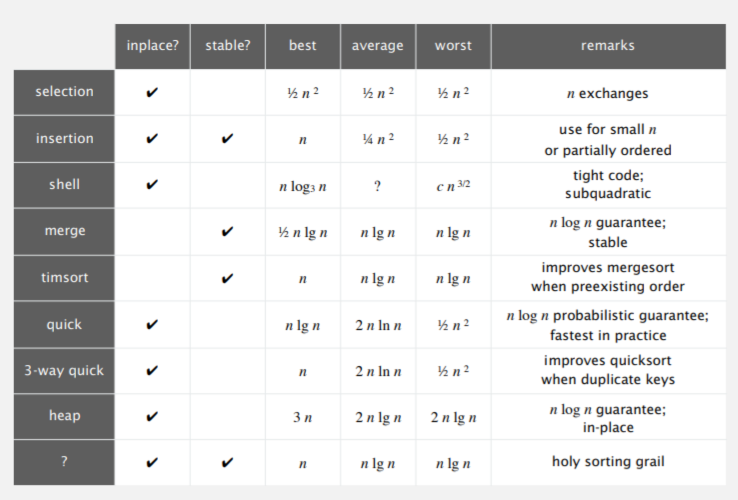
# 2 排序比较
# 5 真题
# 1 前 K 个高频元素
给定一个非空的整数数组,返回其中出现频率前 k 高的元素。
示例 1:
输入: nums = [1,1,1,2,2,3], k = 2
输出: [1,2]
示例 2:
输入: nums = [1], k = 1
输出: [1]
class Solution {
public List<Integer> topKFrequent(int[] nums, int k) {
// build hash map : character and how often it appears
HashMap<Integer, Integer> count = new HashMap();
for (int n: nums) {
count.put(n, count.getOrDefault(n, 0) + 1);
}
// init heap 'the less frequent element first'
PriorityQueue<Integer> heap =
new PriorityQueue<Integer>((n1, n2) -> count.get(n1) - count.get(n2));
// keep k top frequent elements in the heap
for (int n: count.keySet()) {
heap.add(n);
if (heap.size() > k)
heap.poll();
}
// build output list
List<Integer> top_k = new LinkedList();
while (!heap.isEmpty())
top_k.add(heap.poll());
Collections.reverse(top_k);
return top_k;
}}