# LinkList
链表(Linked List)是一种常见的基础数据结构,是一种线性表,但是并不会按线性的顺序存储数据,而是在每一个节点里存到下一个节点的指针(Pointer)。
由于不必须按顺序存储,链表在插入的时候可以达到 O(1)O(1) 的复杂度,比另一种线性表 —— 顺序表快得多,但是查找一个节点或者访问特定编号的节点则需要 O(n)O(n) 的时间,而顺序表相应的时间复杂度分别是 O(log\ n)O(log n) 和 O(1)O(1)。
使用链表结构可以克服数组链表需要预先知道数据大小的缺点,链表结构可以充分利用计算机内存空间,实现灵活的内存动态管理。但是链表失去了数组随机读取的优点,同时链表由于增加了结点的指针域,空间开销比较大。
在计算机科学中,链表作为一种基础的数据结构可以用来生成其它类型的数据结构。链表通常由一连串节点组成,每个节点包含任意的实例数据(data fields)和一或两个用来指向上一个/或下一个节点的位置的链接(links)。链表最明显的好处就是,常规数组排列关联项目的方式可能不同于这些数据项目在记忆体或磁盘上顺序,数据的访问往往要在不同的排列顺序中转换。而链表是一种自我指示数据类型,因为它包含指向另一个相同类型的数据的指针(链接)。
链表允许插入和移除表上任意位置上的节点,但是不允许随机存取。链表有很多种不同的类型:单向链表,双向
链表以及循环链表。
- 链表通常可以衍生出循环链表,静态链表,双链表等。对于链表使用,需要注意头结点的使用
# 1 O(1) 时间内删除链表节点
请编写一个函数,使其可以删除某个链表中给定的(非末尾)节点,你将只被给定要求被删除的节点。
现有一个链表 -- head = [4,5,1,9],它可以表示为
输入: head = [4,5,1,9], node = 5
输出: [4,1,9]
解释: 给定你链表中值为 5 的第二个节点,那么在调用了你的函数之后,该链表应变为 4 -> 1 -> 9.
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* public class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode(int x) { val = x; }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public void deleteNode(ListNode node) {
// ListNoe next = node.next;
node.val = node.next.val;
node.next = node.next.next;
}
}
# 2 反转链表
反转一个单链表。
示例:
输入: 1->2->3->4->5->NULL
输出: 5->4->3->2->1->NULL
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* public class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode(int x) { val = x; }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public ListNode reverseList(ListNode head) {
ListNode pre =null;
ListNode curr = head;
while(curr != null){
ListNode next = curr.next;
// key 保存原链表的下一个节点
curr.next = pre;
pre = curr;
curr = next;
}
return pre;
}
}
# 3 链表的中点
给定一个带有头结点 head 的非空单链表,返回链表的中间结点。
如果有两个中间结点,则返回第二个中间结点。
class Solution {
public ListNode middleNode(ListNode head) {
ListNode slow = head, fast = head;
// key fast的速度快,
while (fast != null && fast.next != null) {
slow = slow.next;
fast = fast.next.next;
}
return slow;
}
}
# 4奇偶链表
给定一个单链表,把所有的奇数节点和偶数节点分别排在一起。请注意,这里的奇数节点和偶数节点指的是节点编号的奇偶性,而不是节点的值的奇偶性。
请尝试使用原地算法完成。你的算法的空间复杂度应为 O(1),时间复杂度应为 O(nodes),nodes 为节点总数。
示例 1:
输入: 1->2->3->4->5->NULL
输出: 1->3->5->2->4->NULL
示例 2:
输入: 2->1->3->5->6->4->7->NULL
输出: 2->3->6->7->1->5->4->NULL
public class Solution {
public ListNode oddEvenList(ListNode head) {
if (head == null) return null;
ListNode odd = head, even = head.next, evenhand = even;
while(even != null && even.next != null){
odd.next = even.next;
odd = odd.next;
even.next = odd.next;
even = even.next;
}
odd.next = evenhand;
return head;
}
}
# 5 排序两个链表
将两个有序链表合并为一个新的有序链表并返回。新链表是通过拼接给定的两个链表的所有节点组成的。
示例:
输入:1->2->4, 1->3->4
输出:1->1->2->3->4->4
class Solution {
public ListNode mergeTwoLists(ListNode l1, ListNode l2) {
// maintain an unchanging reference to node ahead of the return node.
ListNode prehead = new ListNode(-1);
// 用prehead 来保存整个链表, 用prev 来保存最后一个节点。
ListNode prev = prehead;
while (l1 != null && l2 != null) {
if (l1.val <= l2.val) {
prev.next = l1;
l1 = l1.next;
} else {
prev.next = l2;
l2 = l2.next;
}
prev = prev.next;
}
// exactly one of l1 and l2 can be non-null at this point, so connect
// the non-null list to the end of the merged list.
prev.next = l1 == null ? l2 : l1;
return prehead.next;
}
}
# 6 重排链表
给定一个单链表 L:L0→L1→…→Ln-1→Ln ,
将其重新排列后变为: L0→Ln→L1→Ln-1→L2→Ln-2→…
你不能只是单纯的改变节点内部的值,而是需要实际的进行节点交换。
示例 1:
给定链表 1->2->3->4, 重新排列为 1->4->2->3.
示例 2:
给定链表 1->2->3->4->5, 重新排列为 1->5->2->4->3
class Solution {
public void reorderList(ListNode head) {
if (head == null || head.next == null) return;
ListNode p1 = head;
ListNode p2 = head;
// 找到链表的一半
while (p2.next != null && p2.next.next != null) {
p1 = p1.next;
p2 = p2.next.next;
}
// 将链表分为两段
p2 = p1.next;
p1.next = null;
p1 = head;
// 将后半段进行链表的翻转
ListNode head2 = p2;
ListNode next2;
while (p2.next != null) {
next2 = p2.next;
p2.next = next2.next;
next2.next = head2;
head2 = next2;
}
p2 = head2;
// 两条链表进行合并
ListNode next1;
while (p2 != null) {
next1 = p1.next;
next2 = p2.next;
p1.next = p2;
p2.next = next1;
p1 = next1;
p2 = next2;
}
}
}
# 7将有序数组转换成二叉搜索树
给定一个单链表,其中的元素按升序排序,将其转换为高度平衡的二叉搜索树。
本题中,一个高度平衡二叉树是指一个二叉树每个节点 的左右两个子树的高度差的绝对值不超过 1。
示例:
给定的有序链表: [-10, -3, 0, 5, 9],
一个可能的答案是:[0, -3, 9, -10, null, 5], 它可以表示下面这个高度平衡二叉搜索树:
0
/ \
-3 9
/ /
-10 5
- 有序数组是二叉树的中序遍历的结果
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* public class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode(int x) { val = x; }
* }
*/
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode(int x) { val = x; }
* }
*/
class Solution {
private ListNode findMiddleElement(ListNode head){
ListNode pre = null;
ListNode slow = head;
ListNode fast = head;
while(fast != null && fast.next != null){
pre = slow;
slow = slow.next;
fast = fast.next.next;
}
if(pre != null){
pre.next = null;
}
return slow;
}
public TreeNode sortedListToBST(ListNode head) {
// If the head doesn't exist, then the linked list is empty
if (head == null) {
return null;
}
// Find the middle element for the list.
ListNode mid = this.findMiddleElement(head);
// The mid becomes the root of the BST.
TreeNode node = new TreeNode(mid.val);
// Base case when there is just one element in the linked list
if (head == mid) {
return node;
}
// Recursively form balanced BSTs using the left and right halves of the original list.
node.left = this.sortedListToBST(head);
node.right = this.sortedListToBST(mid.next);
return node;
}
}
# 8 删除链表的倒数第N个节点
给定一个链表,删除链表的倒数第 n 个节点,并且返回链表的头结点。
示例:
给定一个链表: 1->2->3->4->5, 和 n = 2.
当删除了倒数第二个节点后,链表变为 1->2->3->5.
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* public class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode(int x) { val = x; }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public ListNode removeNthFromEnd(ListNode head, int n) {
ListNode dummy = new ListNode(0);
dummy.next = head;
ListNode first = dummy;
ListNode second = dummy;
// Advances first pointer so that the gap between first and second is n nodes apart
for (int i = 1; i <= n + 1; i++) {
first = first.next;
}
// Move first to the end, maintaining the gap
while (first != null) {
first = first.next;
second = second.next;
}
second.next = second.next.next;
return dummy.next;
}
}
#
#
# 9 相交链表
编写一个程序,找到两个单链表相交的起始节点。
如下面的两个链表**:**
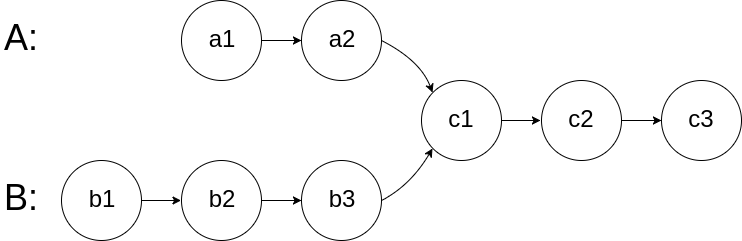
在节点 c1 开始相交。
我们需要做的事情是,让两个链表从同距离末尾同等距离的位置开始遍历。这个位置只能是较短链表的头结点位置。
为此,我们必须消除两个链表的长度差
指针 pA 指向 A 链表,指针 pB 指向 B 链表,依次往后遍历
如果 pA 到了末尾,则 pA = headB 继续遍历
如果 pB 到了末尾,则 pB = headA 继续遍历
比较长的链表指针指向较短链表head时,长度差就消除了
如此,只需要将最短链表遍历两次即可找到位置
public class Solution {
public ListNode getIntersectionNode(ListNode headA, ListNode headB) {
if (headA == null || headB == null) return null;
ListNode pA = headA, pB = headB;
while(pA != pB){
pA = pA==null? headB: pA.next;
pB = pB == null? headA: pB.next;
}
return pA;
}
}
← 字符串 stack-queue →